Project #2: CellPyAbility - High-Throughput Dose-Response Screening
GitHub Repo | PyPI | Bioconda
Built With: Python 3 | Pandas/NumPy/SciPy | CellProfiler | Plotly | PyInstaller | GitHub Actions (CI/CD)
Practical Objective: Automate high-throughput nuclei counting and statistical modeling for in cellulo dose-response assays.
Learning Objective: Build fluency with Python and its data analysis ecosystem. Learn how to design, package, and distribute open-source software.
Featured in Yale School of Medicine News.
Nuclei Counting > Metabolic Proxies for Cell Viability
Standard high-throughput cell viability screens often rely on metabolic proxies (e.g. tetrazolium reduction or ATP content) to estimate cell death. While fast, these methods are often confounded by metabolic variability or redox-active drugs. Further, they lack cell-level resolution, giving a single fluorescent value per well that often loses linearity.
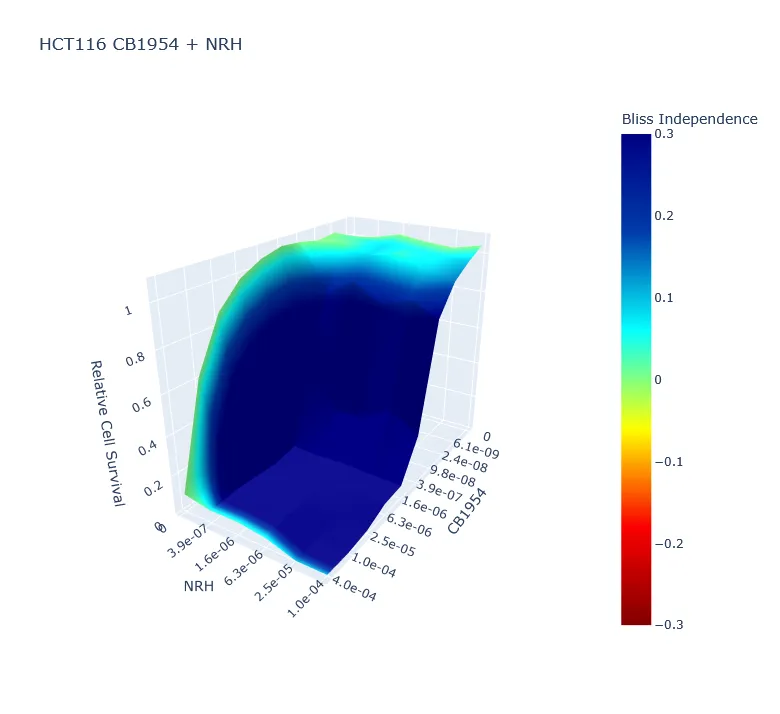
Direct nuclei counting offers a ground-truth measurement of survival with single-cell resolution and higher accuracy. However, the computational cost of analyzing high-content images can be prohibitive. CellPyAbility eliminates this trade-off, processing a 96-well plate in under one minute on commodity hardware. Our software can also analyze 59 unique drug combinations (three 96-well plates) and calculate synergy scores for each combination in under three minutes.
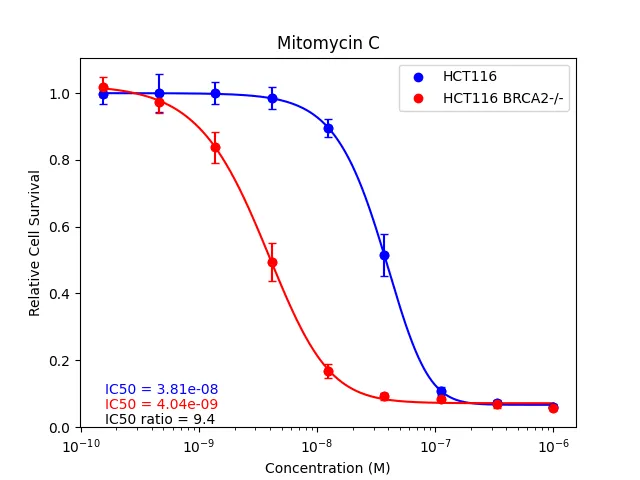
The difference in material cost is also non-trivial: for assessing one 96-well plate, CellTiter-Glo 2.0 costs $30 USD, WST-1 (tetrazolium) costs $16 USD, and our nuclei-counting method costs $0.65 USD. Considering that research projects often require several cell lines, drugs, and biological replicates, the difference in cost can easily reach thousands of USD.
Software Architecture and Accessibility
To ensure accessibility across the technical spectrum, I made two distributions:
- For Computational Biologists: A modular Python package (available via PyPI and Bioconda) integrating CellProfiler for headless image segmentation and NumPy/Pandas/SciPy for statistical analysis.
- For Bench Scientists: A standalone, code-free Windows executable (built with PyInstaller) that bundles the Python runtime and dependencies with an easy-to-use GUI.
Mathematical Implementation
In addition to normalization and summary statistics, CellPyAbility consists of two core analytical modules for biological inference:
- Logistic Regression: The GDA (growth delay assay) module fits dose-response curves using a 5-parameter logistic (5PL) model, then solves for the IC50 for each condition. Depending on the experiment, the ratio of IC50s can be used as an approximate therapeutic index.
- Synergy Modeling: The Synergy module models 59 unique drug interactions per experiment. It calculates Bliss Independence scores and renders interactive 3D surface maps using Plotly to visualize synergistic volumes.